Astrophysics > 4. Determining Distance >
Define absolute and apparent magnitude
- Brightness: The intensity of light emitted by and object in a particular direction.
- Magnitude: A measure of the brightness of a celestial object.
- The ancient Greek astronomer Hipparchus established a magnitude scale to record the brightness of stars:
- The brightest visible stars were given a magnitude of 1.
- The faintest visible stars were given a magnitude of 6.
- An extension of this scale is still used today.
- Since Hipparchus established his scale, stars have been found that are brighter than magnitude 1 and dimmer than magnitude 6.
- In the 1850s, scientists discovered that the human eye did not respond to light linearly.
- A magnitude 1 star is approximately 100 times brighter than a magnitude 6 star.
- A one unit difference in magnitude corresponds to a 5√100 or 2.512 difference in brightness.
- The brightness ratio of two celestial objects and the difference between the magnitude of the objects are related by the formula:
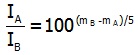
- Apparent Magnitude (m): The magnitude of a celestial object as viewed from Earth.
- Absolute Magnitude (M): The magnitude of a celestial object were it viewed from a standard distance of 10 parsecs.
