From Ideas to Implementation > 4. Photoconductivity >
Describe the occurrence in superconductors below their critical temperature of a population of electron pairs unaffected by electrical resistance
- Just as increased temperature increases resistance, so decreased temperature decreases resistance.
- Superconductivity: The potential of a material to allow electrons to flow unimpeded, having an effective resistance of zero, at certain low temperatures.
- Critical Temperature (TC): The temperature at which a material becomes a superconductor.
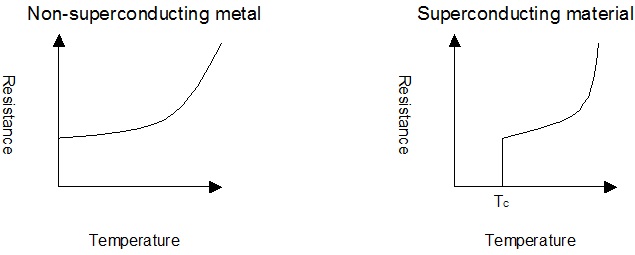
- As the temperature of a superconducting material drop below the critical temperature, lattice effects begin to assist instead of impede electron flow.
- This assistance comes from an effect that pairs electrons, with this phenomenon being part of the BCS theory.
