Einstein’s equation states that if m amount of mass was completely converted to energy, the total amount of energy released would be E = mc2
- In fusion reactions, the final products have a lighter total mass than the total mass of original products.
- This is called the mass defect , denoted by

- The energy released can be calculated as
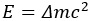
- The earliest understanding of what provides energy in the stars came when Cecilia Payne , using spectroscopy discovered that Sun is composed mostly of Hydrogen .
- The extreme heat in the sun due to change of gravitational potential energy to thermal energy, releases the electrons from the atoms and creates a ball of plasma , ionised hydrogen and helium nuclei.
- One possible nuclear reaction could provide energy to the stars was the proton-neutron fusion.
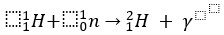
- The deuteron formed has less mass than the original proton and neutron .
- This mass defect is converted to energy, according to the equation
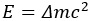 .
. - The energy released with every fusion is about 2.2 MeV
- But this reaction cannot be the major source of energy as there aren’t enough neutrons in the stars to sustain the reaction.
- Since majority of the element in the stars are Hydrogen atoms, proton-proton fusion is likely the major cause of energy release.
- Although proton-proton electrostatic repulsion is very strong, the extreme conditions in stars help the protons overcome this force and get close enough for strong nuclear force to act.
- As they fuse the to form deuterium, the electrostatic repulsion doesn’t play a part anymore as one of the protons change into a neutron.
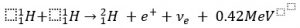
- The energy released comes from the difference in mass of the original products from the final products, according to the equation :
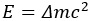
- The positron gets annihilated by an electron :

- The deuterium then further fuses with another proton to form Helium

-
- Depending on the condition of the star (temperature and pressure) , the
 may fuse to form
may fuse to form  through various intermediary steps.
through various intermediary steps.
- Depending on the condition of the star (temperature and pressure) , the
Extract from Physics Stage 6 Syllabus © 2017 NSW Education Standards Authority (NESA)
